In the realm of clinical presentation, right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain stands as an enigmatic and intricate entity that perplexes healthcare professionals and patients alike. Positioned at the intersection of multiple organs and structures, the RUQ harbors a delicate network of vital anatomical components, making any discomfort within this region a matter of profound significance. This article explores the common causes of upper abdominal pain, focusing on gastrointestinal and kidney problems. It also discusses the diverse symptoms associated with RUQ pain.
Right Upper Quadrant Pain Symptoms & What to Do:
It is important to seek immediate medical attention for severe RUQ pain accompanied by symptoms such as fever, persistent vomiting, tender abdomen, blood in stool, etc. Additional preventive measures to mitigate the risk of RUQ pain include maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, regular exercise, limiting alcohol intake, practicing good hygiene, etc.
By gaining insights into the causes, symptoms, and preventive strategies for RUQ pain, individuals can proactively care for their health and seek appropriate medical assistance.
What Is The Right Upper Quadrant?
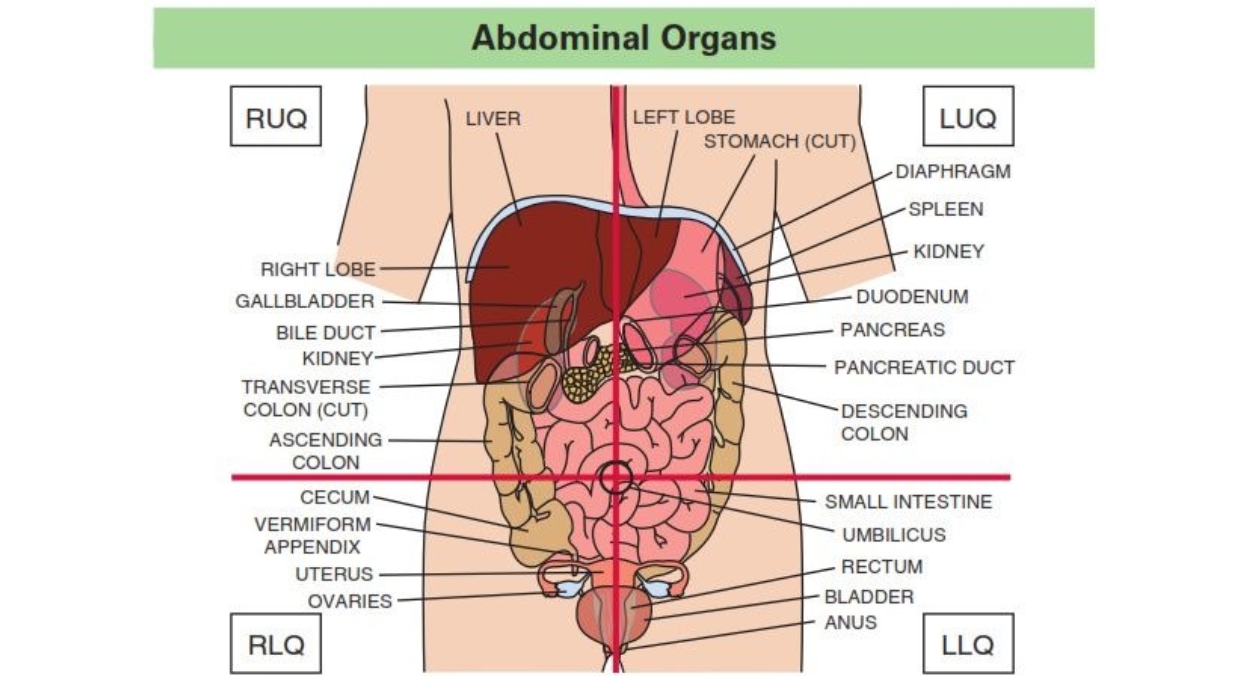
The RUQ region of the abdomen contains vital anatomical structures, including the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, pancreas, and parts of the small and large intestines. Understanding this region’s intricate anatomy and physiology can help identify the underlying causes of RUQ pain.
Symptoms Of Upper Right Abdominal Pain
RUQ pain can present with diverse symptoms, and the specific manifestations depend on the underlying condition causing the pain. One of the common sensations associated with RUQ pain is the dull, aching sensation.
This type of pain is typically persistent and may indicate chronic conditions such as liver or gallbla RUQ pain candder inflammation. On the other hand, sharp or stabbing pain in the RUQ can suggest acute conditions like gallstones or kidney stones. These types of pain are often intense and may come in waves.
Referred pain is another noteworthy aspect of RUQ pain. It occurs when the pain originating in the RUQ is felt in other areas of the body, such as the shoulder or back. Referred shoulder pain is commonly associated with conditions affecting the gallbladder.
Common Causes Of Upper Abdominal Pain

Unraveling the underlying causes of this abdominal discomfort requires a comprehensive understanding of the diverse pathologies that can manifest within the RUQ. This article lists common causes of RUQ pain.
Proper evaluation by a medical professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. An individual’s symptoms should be assessed with a medical history, physical examination, and further diagnostic tests to determine the underlying condition responsible for the RUQ pain.
- Common: Acute Cholecystitis, Gallstones, Acute Hepatitis, Hepatic Steatosis (Fatty liver), Ascending Cholangitis, Acute Pancreatitis, Duodenal Ulcer.
- Less Common: Acute Colitis, Appendicitis, Omental Infarct, Hepatic Pyogenic Abscess, Passive Hepatic Congestion, Diverticulitis, Pyelonephritis, Thoracic Infection, Hepatic Tumor.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder, located beneath the liver, is crucial in storing and releasing bile for digestion. Gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, are the most common causes of RUQ pain. These stones can obstruct bile flow, leading to bile accumulation in the gallbladder. This results in enlargement, increased pressure, and irritation of the gallbladder and surrounding tissues, which can ultimately lead to cholecystitis.
Approximately 90-95% of patients with cholecystitis have gallstones. Around 10% of the population in North America has gallstones. RUQ pain associated with gallstones is typically described as a colicky or cramp-like sensation, often radiating to the back or right shoulder. The intensity and duration of the pain can vary depending on the size and location of the gallstones.
Liver
The liver, the largest solid organ in the body, dominates the RUQ. It performs essential functions such as metabolism and detoxification. Liver inflammation, known as hepatitis, can stretch the protective capsule surrounding it, leading to pain in the upper right quadrant. Hepatitis can result from various causes, including viral infection, alcoholic, drug-induced, or toxin-induced.
Furthermore, usually asymptomatic, fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis), as the name implies, is characterized by too much fat buildup in the liver. It becomes a problem when the fat reaches around 5-10% of the liver’s weight.
This causes an enlarged liver and RUQ pain. Liver-related RUQ pain is typically described as a dull, aching sensation. It may be accompanied by other symptoms such as jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), fatigue, nausea, and loss of appetite.
Biliary Ducts
Biliary ducts can also be inflamed, causing potentially life-threatening acute or ascending cholangitis. The bile ducts are tubes that connect the gallbladder to the liver that carries bile, a fluid that digests foods and breaks down fat. Acute cholangitis occurs when bacteria ascend and infect the biliary tree.
The primary instigator behind this condition is often choledocholithiasis, which refers to the presence of infection-causing stones in the common bile duct. These stones can cause complete or partial obstruction of the biliary system, leading to cholangitis.
Duodenum of the Small Intestines
Furthermore, the duodenum, the first part of the small intestines responsible for absorbing nutrients and water from food for the body, can also be ulcerated. A duodenal ulcer is a sore that damages the mucus barrier of the duodenal lining.
The main cause of this damage is an infection with bacteria called H. Pylori. Lifestyle factors such as smoking, drinking alcohol, increased intake of fatty foods, and spicy and acidic foods increase an individual’s risk for duodenal ulcers.
Right Kidney
The right kidney, part of the urinary system, is also in the RUQ. It filters waste products and excess fluids from the blood, producing urine. The kidney can cause upper right abdominal pain if affected by conditions such as kidney stones or kidney infections.
Kidney stones can cause RUQ pain due to referred pain. A stone in the right kidney can obstruct urine flow, leading to pressure and distension. The irritation stimulates nearby nerves, causing the pain that is felt in the RUQ. The intensity and location of the pain can vary depending on the size and location of the kidney stone within the urinary system.
A kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, can cause RUQ pain. The infection usually starts in the lower urinary tract (urinary tract infection) and ascends to the kidneys. As the infection progresses, it can lead to inflammation and swelling of the kidney tissue. This inflammation can stimulate nerve endings, resulting in pain perceived in the RUQ.
When To Seek Medical Attention For Upper Right Abdominal Pain
RUQ pain can vary in intensity and duration, and certain symptoms may signify an emergency, requiring immediate medical attention. If you experience any of one of the following, it is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Fever: the temperature at or above 100.4F.
- Persistent vomiting, esp. vomiting blood or what looks like coffee grounds.
- Nausea
- Tender abdomen: pain gets worse when you touch your abdomen.
- Blood in stool
- Sweating
- Fast heartbeat
- Confusion
- Unexplained unintentional weight loss
- Yellowish of the skin – jaundice
Prevention Of Right Upper Quadrant Pain
Preventing RUQ pain involves addressing the underlying issues and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are some preventive measures:
- Maintain a balanced diet: Eat a healthy diet of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit the consumption of fatty, fried, and processed foods, which can contribute to gallstone formation and liver problems.
- Stay hydrated: Drink adequate water throughout the day to promote proper digestion and prevent dehydration.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight, improve digestion, and promote overall well-being.
- Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver.
- Practice good hygiene: Maintain good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, especially before meals.
- Avoid excessive use of medications: Certain medications, when used excessively or without proper medical supervision, can cause damage to the organs of the RUQ. Follow prescribed dosages and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can lower your immune system, which increases your susceptibility to infections.
Conclusion
RUQ pain can be a distressing symptom caused by various conditions affecting organs in the abdominal region. Understanding the underlying causes and recognizing the specific symptoms of RUQ pain is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Prompt medical evaluation is essential, especially when severe or alarming symptoms occur. Individuals can reduce the risk of developing RUQ pain by adopting preventive measures. Ultimately, staying proactive about your health can improve overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of experiencing RUQ pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
The cause of your abdominal pain determines your treatment. Your doctor will perform tests, including a physical examination. They will check for masses, muscle contraction, tightness, and sensitivity to touch. Additional tests may include CT scans, ultrasound, blood tests, and urine tests.
Severe abdominal pain is characterized by rapid onset intense pain. The sudden and acute nature of the pain typically indicates a serious underlying condition or medical emergency.
