Weight loss comes with numerous benefits,[1] including better health and well-being. That’s why many people strive to find tactics to shed extra pounds. Today, there are numerous ways to lower body mass index, such as Wegovy and Ozempic pills.
It’s common to wonder how long you should take Wegovy or semaglutide for weight loss[2] and chronic weight management. Frankly, the results for people who use Wegovy for weight loss vary. However, clinical trials that show people losing weight fast do exist.Perhaps you’ve tried diet pills or fat burners, and nothing works. Research shows that Wegovy is effective for weight loss. A healthcare provider is the only person who can prescribe Wegovy to maintain weight loss. In this article, you can learn more about the drug treatment and how long it takes Wegovy to work.
How Long Do You Need To Take Wegovy?
You need to take Wegovy for at least 68 weeks to see significant weight loss. It’s a long-term chronic weight management treatment.
How Long Do You Take Wegovy For Weight Loss?
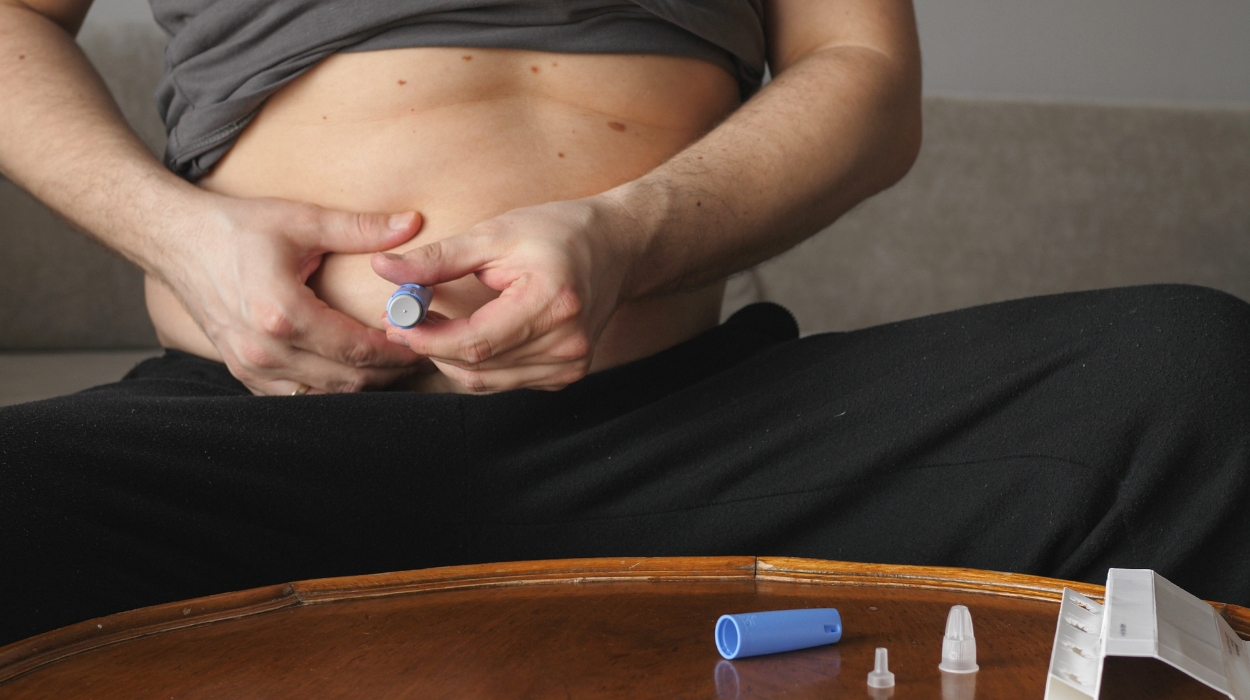

The duration for Wegovy as a weight loss treatment varies. One factor to consider is the amount of excess weight you need to lose to achieve your health goals. It also depends on your lifestyle choices, activity level, and preexisting health conditions.
Based on existing studies, Wegovy continues to show positive results in terms of body weight compared to placebo. One clinical trial[3] included a group of 1961 adults with a high body mass index and some with weight-related health conditions.
This clinical trial lasted for 68 weeks and had two groups. One group received a semaglutide injection once a week, while the other got a placebo and lifestyle intervention. The results showed that 83% of those who took Wegovy lost 5%[3] or more body fat.
In terms of duration, there’s no set time to see results from Wegovy. However, evidence shows that a 68-week treatment[4] can lead to up to 15% loss in body mass percentage. Other research shows weight plateauing[5] after 60 weeks of treatment.
Successful weight loss can take time, but it’s possible. Work on making lifestyle changes[6] to see better results. For example, eat a calorie deficit, consume healthy foods, and engage in more physical activity.
How Does Wegovy Work
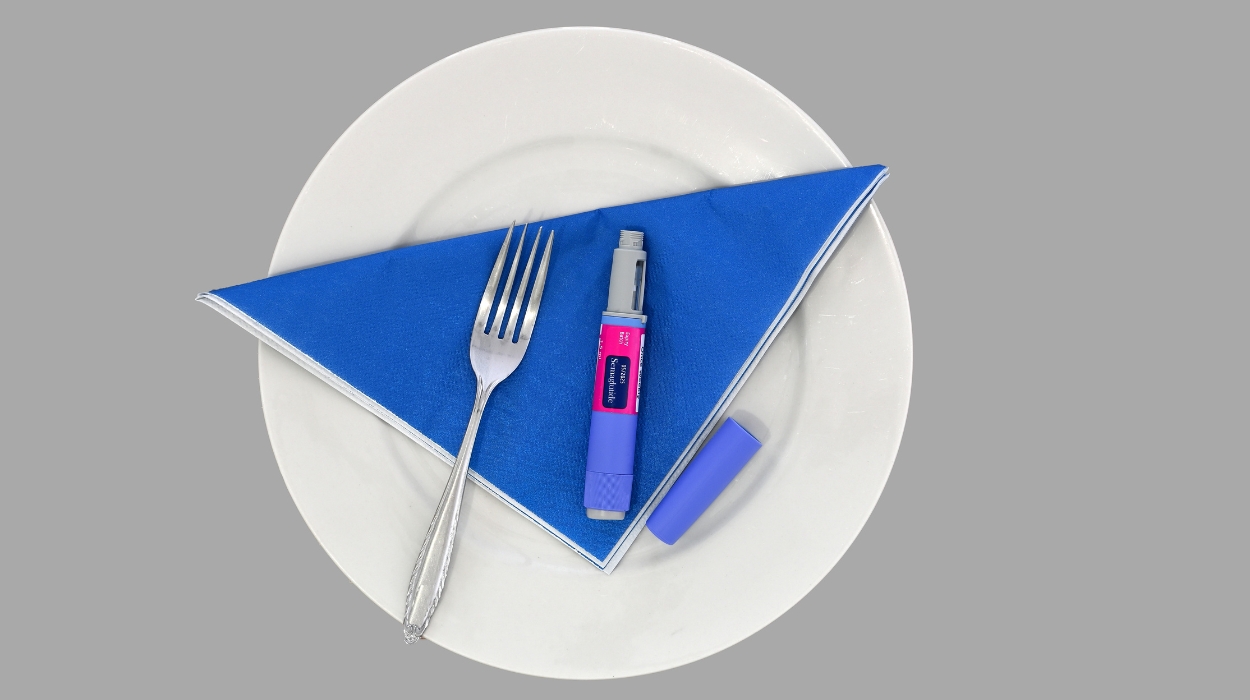

A healthcare provider can prescribe Wegovy for a weight-related medical condition. Wegovy is the brand name for semaglutide, a drug that belongs to the class of medications known as glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists.
Such medications imitate hormones naturally released by the body that help you lose weight. Semaglutide causes the pancreas to release sufficient insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.[7] People with type 2 diabetes take semaglutide to control their blood sugar.
There are three ways in which Wegovy can help you achieve weight loss.
Delayed Stomach Emptying
An empty stomach makes it harder to resist eating. Since Wegovy works to delay stomach emptying,[5] food remains in your stomach longer. This makes you feel less hungry, decreasing food consumption and achieving more weight loss.
Just make sure to consult a healthcare provider before taking Wegovy.
Appetite Suppression
As you think about how long you need to take Wegovy for weight loss, it’s good to know how the drug helps you lose weight. Another way in which weight management is possible is through appetite suppression.[8]
Wegovy targets the area in the brain[9] that’s responsible for your appetite. As a result, you feel fuller longer and are less likely to give in to food cravings.
Regulate Blood Sugar
Anyone who wants to lose weight can benefit from regulating blood sugar levels. High blood sugar, for example, can lead to weight gain and food cravings. Evidence shows that blood sugar regulation[10] helps control insulin resistance.
The CDC estimates that there are 38 million people[11] in the U.S. who have type 2 diabetes. These people must find ways to manage their blood sugars for better health. Otherwise, low or high blood sugar levels can lead to serious issues.
When you want to lower blood sugar levels, taking Wegovy can help. It lowers the amount of glucose[12] in the blood after food intake. That’s why diabetes patients[13] on Metformin can get Wegovy doses for blood sugar regulation.
How Long Does It Take For Wegovy To Work?
Wegovy weight loss results vary, but you need a lifestyle intervention like more physical activity and a hypocaloric diet to achieve set weight loss goals.
However, it’s important to note that some people take longer to start losing weight.[14] Allow your body to adjust, and take your weight loss journey. Wegovy can require long-term treatment to achieve weight goals along with escalating doses.
One study shows some people do experience weight gain[15] after they stop taking Wegovy. So, consult your healthcare provider about long-term use to achieve weight loss. You should also explore sustainable lifestyle changes that can maintain your healthier weight after you stop taking Wegovy.
Remember, weight loss is not a linear journey. When you start taking Wegovy, you may experience rapid weight loss[16] initially, but it can slow down after a certain duration. This change in pace is typical of any weight loss journey and underscores the need for a holistic approach involving diet, exercise, and mental health in addition to taking medications.
Who Should Take Wegovy?
After learning more about Wegovy, it’s also good to understand who should take Wegovy for weight loss. Wegovy is a new drug treatment that got FDA approval[17] in 2021 for chronic weight management treatment.
The FDA approved Wegovy injection in adults suffering from obesity with a BMI of 30 or a BMI of 27 and at least one weight-related condition like high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol. Dosages are usually initiated at .25 mg weekly for four weeks and titrated upwards. Patients often get 2.4 milligrams[18] weekly for 65 to 70 weeks.
Healthcare providers prescribe Wegovy to those who are obese and need to lose a significant amount of body fat. If you have weight-related conditions like high blood pressure[19] or high cholesterol, losing weight is crucial for your health. Wegovy is handy in weight loss, especially if you can’t engage in lots of physical activity.
Making healthy food choices and engaging in more physical activity helps to maintain weight loss. Steps to change your lifestyle should begin in the early weeks of Wegovy titration. During that time, learn how many calories to lose weight and inquire whether to take weight loss supplements.
Side Effects of Wegovy Drug Treatment
It’s important to note side effects when taking Wegovy for weight loss. You can experience mild or serious side effects such as
- Diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain.[2]
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Headache.
- Upset stomach.
- Acid reflux.
- Hair loss.
- Fatigue.
There are ways to manage mild side effects, and some won’t last long. However, if symptoms persist, see your health practitioner.
Chronic side effects when using Wegovy to lose weight include:
- Pancreatitis.
- Low blood sugar.[20]
- Rapid heart rate.
- Gallstones.
Contraindications
Wegovy is contraindicated with some medications.
Taking both insulin and Wegovy shots puts you at risk of hypoglycemia. Your doctor may adjust your insulin dose before you go on Wegovy.
Another medication that can interact with Wegovy is meglitinides,[21] a type of oral diabetes medication. The other type is sulfonylureas,[22] a type of diabetes oral drugs such as glyburide and glipizide.
Conclusion
Wegovy doses are becoming popular as a way to treat chronic weight issues such as obesity. The semaglutide injection helps to jumpstart your weight loss journey. People take weekly doses for a duration set by a healthcare provider.
Wegovy can help boost weight loss by delaying stomach emptying, suppressing appetite, and regulating blood sugar levels. Wegovy enables you to lose significant weight, but the duration varies from one person to the next.
Finally, remember that taking Wegovy is just the first step for a successful, healthy, and long-lasting weight loss journey. Consult with your healthcare provider to develop lifestyle improvements that can help you keep your weight off with and without Wegovy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wegovy can lead to good results, but it’s not for everyone. People suffering from conditions such as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome, semaglutide allergy, or allergic to any Wegovy ingredients.
Always follow the healthcare provider’s instructions when you start taking Wegovy shots. After your first shot, you may experience mild side effects such as diarrhea and nausea.
Ozempic and Wegovy are both effective drug treatments for chronic weight management. However, be sure to consult your doctor to determine which one works best for you.
You can start to see results within a few weeks. However, it’s important to note that results can vary from one person to the next. Adding better lifestyle habits like healthy foods and physical activity can affect the rapidity of results.
Weight loss can vary from one person to the next. However, it’s possible to lose up to 8% body fat[2] after two months with Wegovy injections.
 Evidence Based
Evidence Based