In today’s fast-paced world, where stress and unhealthy lifestyle choices have become the norm, it’s no surprise that high blood pressure has become a common health concern.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition that impacts millions of people across the globe. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of your blood vessels is consistently too high. While medication and lifestyle changes are often recommended to lower blood pressure, natural supplements can also be valuable to your wellness routine.
Can Supplements Help Lower Blood Pressure?
Supplements work to lower blood pressure by targeting the various factors that contribute to hypertension. They can help relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce inflammation. It’s important to note that while these supplements can be beneficial, they should not replace prescribed medication or medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Causes Of High Blood Pressure
Understanding the common causes of high blood pressure is the first step toward managing it effectively. Several factors can contribute to hypertension, including:
- Poor diet.
- Lack of exercise.
- Smoking.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Chronic stress.
- Genetics.
- Underlying medical conditions.
- Certain medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), birth control pills, antidepressants, and decongestants.
High Blood Pressure Basics
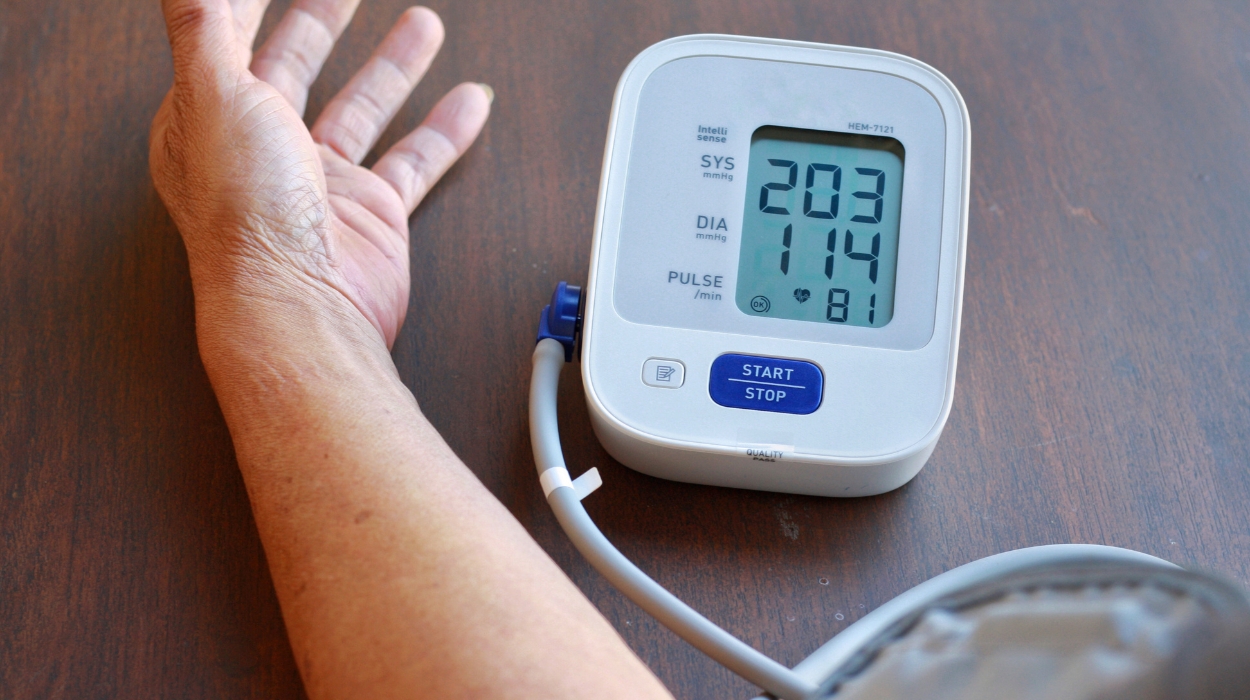
High blood pressure is often called the “silent killer” because it typically doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms until it reaches a severe stage or results in heart disease, kidney disease, or stroke. Some individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Headaches.
- Dizziness.
- Blurred vision.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain.
- Irregular heartbeat.
Regular blood pressure checks are essential to monitor your levels and detect potential issues early on.
What Are Healthy Blood Pressure Levels?
Both systolic and diastolic pressures are important in determining an individual’s overall blood pressure status. An elevated reading in either category may indicate hypertension, and you should monitor and manage your blood pressure accordingly.
- Systolic Blood Pressure: The first number in a blood pressure reading represents systolic pressure. It measures the force exerted on the artery walls when the heart contracts and pumps blood into circulation. Normal blood pressure is typically around 120 mmHg or lower for systolic readings. Scientists consider readings over 130 mmHg “high blood pressure.”
- Diastolic Blood Pressure: The second number in a blood pressure reading reflects diastolic pressure. It measures the force exerted on the artery walls when the heart is at rest between beats, filling with blood. Normal diastolic blood pressure is generally around 80 mmHg or lower. Scientists consider any readings over 80 mmHg “high blood pressure.”
A blood pressure reading states systolic pressure first, followed by diastolic pressure. For example, if a person’s blood pressure is recorded as 120/80 mmHg, 120 is the systolic pressure, and 80 is the diastolic pressure.
The Stages Of Hypertension
Researchers divide blood pressure levels into four categories: normal, elevated, stage 1, and stage 2:
- Elevated blood pressure is the first indication of hypertension. Consistently elevated blood pressure readings ranging from 120-129 mmHg systolic and less than 80 mmHg diastolic characterize elevated blood pressure. While not officially considered hypertension, elevated blood pressure suggests an increased risk of developing hypertension in the future.
- Stage 1 hypertension is diagnosed when blood pressure consistently ranges from 130-139 mmHg systolic or 80-89 mmHg diastolic. At this stage, medical professionals recommend lifestyle modifications or blood pressure medication.
- Stage 2 hypertension occurs when blood pressure consistently measures 140-180 mmHg systolic or 90 – 120 mmHg diastolic. At this stage, more aggressive treatment is necessary to effectively manage blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
Medical professionals classify blood pressure readings over 180 mmHg systolic or over 120 mmHg diastolic as a “Hypertensive Crisis” requiring immediate medical consultation.
6 Supplements Help Lower Blood Pressure 2024

Several dietary supplements can help reduce blood pressure levels, including omega-3 fatty acid fish oil, magnesium, Coenzyme Q10, hibiscus, calcium, and potassium. Each of these blood pressure supplements works through different mechanisms.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that offer numerous health benefits, including their potential to lower blood pressure. You can find these healthy fats in certain fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, as well as in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-3 fish oil supplements are also widely available and can provide an additional boost to your heart health.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral crucial in various bodily functions, including maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. It helps relax and widen blood vessels, allowing for better blood flow. Some dietary sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. If your magnesium levels are low, your healthcare provider may recommend a magnesium supplement.
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10, also known as CoQ10, is a powerful antioxidant supporting cardiovascular health. It helps improve cellular energy production and can reduce blood pressure levels. CoQ10 is naturally present in organ meats, fatty fish, and whole grains. However, supplementation can be beneficial since it can be challenging to obtain optimal levels through diet alone.
Hibiscus Sabdariffa
Hibiscus sabdariffa, also known as Roselle, is a flowering plant that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to manage blood pressure. It contains compounds that have been shown to have a mild diuretic effect and help relax blood vessels. Hibiscus tea or dietary supplements made from its extract can be a natural and refreshing way to support healthy blood pressure levels.
Calcium
Calcium is not only essential for maintaining strong bones but also for regulating blood pressure. It helps blood vessels contract and expand properly while also playing a role in nerve signaling. Though it’s best to obtain calcium from dietary sources such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods, medical professionals may recommend calcium supplements if your levels are low.
Potassium
Potassium is a mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. It helps to balance the sodium in our bodies, which is essential for regulating blood pressure. Potassium acts as a natural diuretic, promoting the elimination of excess sodium and water from the body, thereby lowering blood volume to reduce blood pressure. Additionally, potassium supplements help to relax and dilate blood vessels, allowing for smoother blood flow and reducing strain on the cardiovascular system.
Other Tips To Reduce High Blood Pressure
In addition to incorporating natural supplements into your routine, there are several other lifestyle changes you can make to regulate blood pressure:
- Eat a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Limit your sodium intake by limiting processed foods and opting for low-sodium alternatives.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga.
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking and other tobacco products.
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and regular exercise.
When To See A Doctor
While natural supplements and lifestyle changes can be effective in reducing blood pressure for many individuals, it’s essential to seek medical advice if you’re experiencing persistent high blood pressure. Your doctor might choose to prescribe blood pressure medications or make specific lifestyle adjustments.
Additionally, you should seek immediate medical attention for systolic blood pressure readings over 180 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure readings over 120 mmHg when combined with any of the following symptoms:
- Abnormal headache.
- Shortness of breath.
- Vision changes.
- Chest pains.
- Changes in speech.
- Weakness or numbness/tingling.
Conclusion
Taking control of your health and managing high blood pressure is within your reach. By incorporating supplements into your daily routine, making positive lifestyle changes, and seeking medical advice when needed, you can promote healthy blood pressure levels and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. Remember, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider before taking any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet or exercise regimen.
Frequently Asked Questions
The answers to these frequently asked questions about supplements and blood pressure levels may help provide you with additional insight.
Natural supplements can be beneficial for managing blood pressure. However, they should not replace prescribed medication or medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The time it takes for supplements to lower blood pressure can vary depending on the individual and the specific supplement. It’s important to be patient and consistent with your supplement routine and monitor your blood pressure levels regularly.
Most natural supplements are considered safe when taken as directed. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects like digestive issues or allergies. If you experience any adverse effects, discontinue use and consult with your healthcare provider.
Certain supplements, like omega-3 fatty acids and magnesium, have been shown to positively affect both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
Natural supplements can be effective for many individuals with high blood pressure. However, everyone’s body is unique, and results may vary. Working closely with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for managing your blood pressure is essential.
