Flabby arms are a common issue typically caused by a build-up of subcutaneous fat or loose skin in the upper arm region. Upper arm fat is not necessarily unhealthy, but often it has a negative impact on how people feel about their appearance. As a result, many people want to know how to lose upper arm fat and tone their biceps.
Read on for our best tips on how to lose arm fat and increase muscle mass with cardiovascular and strength training exercises.
How To Get Rid Of Arm Fat: The Best Exercises
- Cardiovascular exercise.
- Arm Circles.
- Bicep Curls.
- Triceps Dips.
- Push Ups.
How To Lose Arm Fat Fast?
Lots of people want to know how to get rid of arm fat, but it can be difficult to spot and reduce body fat. Some people can melt arm fat simply by losing weight, as shedding pounds can shrink pockets of fatty tissue and reduce arm circumference. However, for people whose flabby arms are caused by loose skin, strength training exercises that tone the upper body in addition to general weight loss may be more effective.
Cardio Exercises

Upper arm fat is considered subcutaneous fat. It sits just under the skin and can be pinched with your fingers. Many fit and healthy people struggle with upper arm fat, with the problem even more pronounced in overweight individuals. If you are overweight or obese you can slim down your upper arms by reducing your overall body fat percentage, and the best way to lose fat is with cardio.
Cardiovascular exercise, also called aerobic exercise, is any form of physical activity that raises your heart rate[1] and activates the large muscles in your body. High-intensity cardio efficiently burns calories and is highly effective[2] for fat loss. Therefore, regular cardio workouts can help you to lose weight from every part of your body, including your upper arms.
If you are embarking on a weight loss journey, choosing a form of exercise you enjoy is key to success. Popular forms of cardio include dancing, jogging, hiking, swimming, cycling, and team sports. The best way to build your fitness level is to start with gentle or moderate exercise and increase the intensity of your workouts as your stamina improves.
Arm Circles
Not everyone with chubby arms is overweight. If you are generally slim but struggle with excess arm fat or loose skin, you may be able to reduce the problem by building up your arm muscles. Arm circles are a good starting exercise for people who want to improve their arm strength but aren’t yet ready for weight training.
Adding arm circles to your exercise routine can strengthen and tone the biceps and triceps muscles in your upper arms. Building muscle mass in your arms can help tighten flabby skin and reduce excess body fat for more toned, sculpted upper arms.
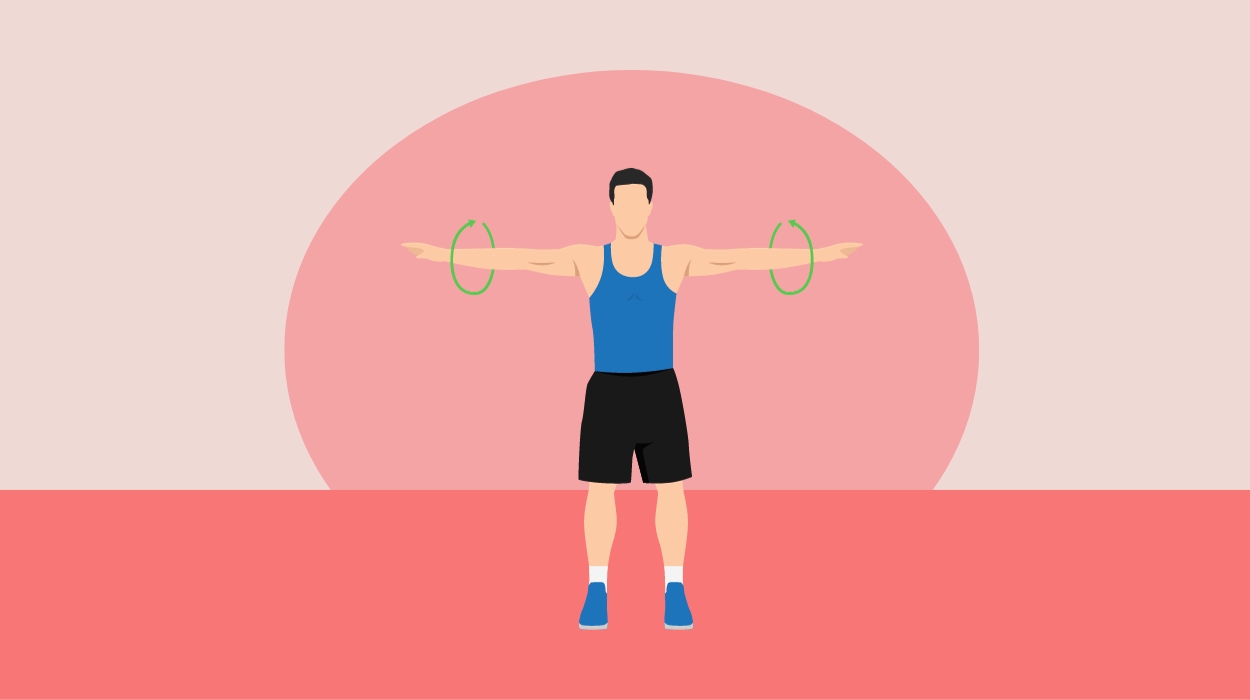

How To Do:
- Stand up straight and extend your arms straight out to each side of your body while keeping your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Slowly rotate your arms from the shoulders, keeping your arms straight and elbows locked.
- Repeat this movement ten to twenty times, changing direction halfway through each set of circles.
Tips:
- Maintain a controlled and continuous circular motion to target your shoulder muscles effectively.
- Begin with smaller circles to warm up your shoulders and reduce the risk of injury.
- Inhale as your arms come forward and exhale as they move backward to maintain rhythm and focus during the exercise.
Optimal Sets & Reps: 3 sets of 10-15 reps.
Bicep Curls
Weight training (or resistance training) can reduce body fat[3] and increase lean body mass, which helps create a slimmer, more athletic physique. Arm exercises like bicep curls involve weights, which can build muscle mass in your upper arms and make them more firm.
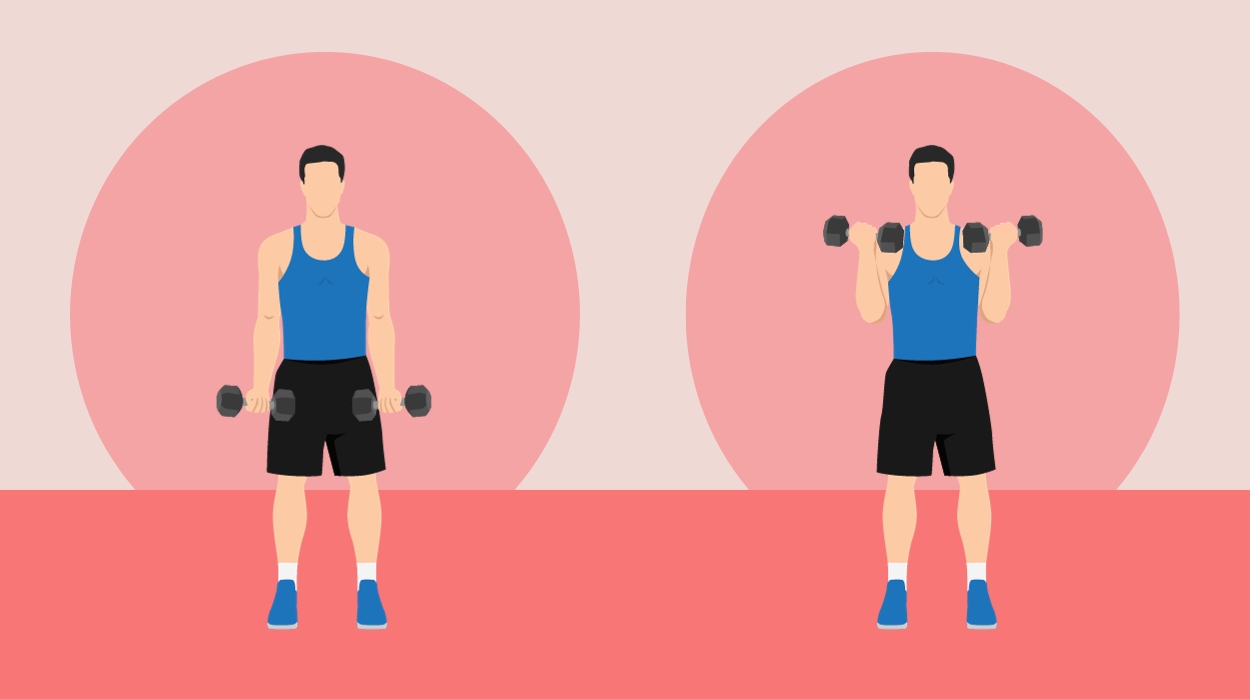
How To Do:
- Select an appropriate set of dumbbells
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and a weight in each hand. Your arms should be by your sides, your shoulders should be relaxed, and your palms should face forward.
- Bend your arms at the elbows and lift both dumbbells toward your shoulders while keeping your elbows tucked into your sides.
- Lower the dumbbells back down to their starting position.
Tips:
- Start with lightweight dumbbells, such as two to five kilograms, and increase the weight as your strength improves.
- Ensure your elbows stay close to your body as you curl the weights to fully engage your biceps.
- Avoid swinging the weights or using momentum.
Optimal Sets & Reps: 3 sets of 10 reps
Triceps Dips
The triceps are large, thick muscles that extend from your armpit to your elbow. Unlike the biceps on the front of the upper arm, the triceps are positioned on the underside of the upper arm where excess fat and skin often accumulate. Toning up your triceps can, therefore, tighten the skin[4] of the upper arms and help reduce the appearance of bat wings.
Triceps dips involve raising and lowering your whole body using your triceps muscles.
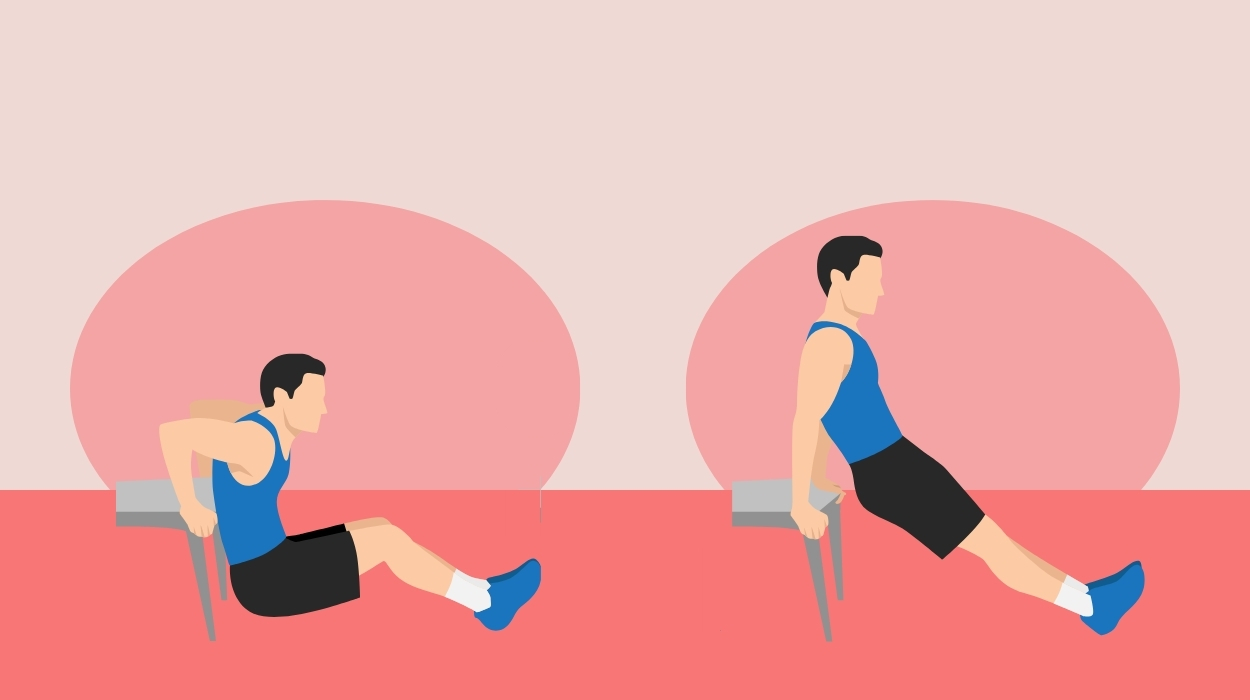

How To Do:
- Choose something sturdy to support your weight, like a bench or chair.
- Stand in front of your bench or chair and bend your knees, leaning back until your hands rest on the surface behind you. Get a good grip on the surface by curling your fingers around the edge and shuffle your feet forward until your legs are straight. Most of your weight should now be resting on your hands.
- Begin to lower your body down by bending your arms at the elbows. When your upper arms are parallel to the ground, pause for a second before using your triceps to push your body back up to its starting position.
Tips:
- Keep your core muscles engaged throughout the exercise to stabilize your body and avoid excessive swaying or arching of the back.
- Maintain proper hand placement to provide stability and target your triceps effectively.
- Avoid jerky or rapid movements to reduce the risk of injury and maximize muscle engagement.
Optimal Sets & Reps: 3 sets of 10-15 reps.
Push-Ups
Push-ups are a type of strength training exercise that builds muscle mass in the upper body, making them a great choice for toning flabby arms. These exercises activate the pectoral muscles, shoulder muscles, and triceps[5] and may reduce the appearance of fat tissue and loose skin around the arms. As an added bonus, push-ups also engage the core muscles and can help sculpt and strengthen your abs.
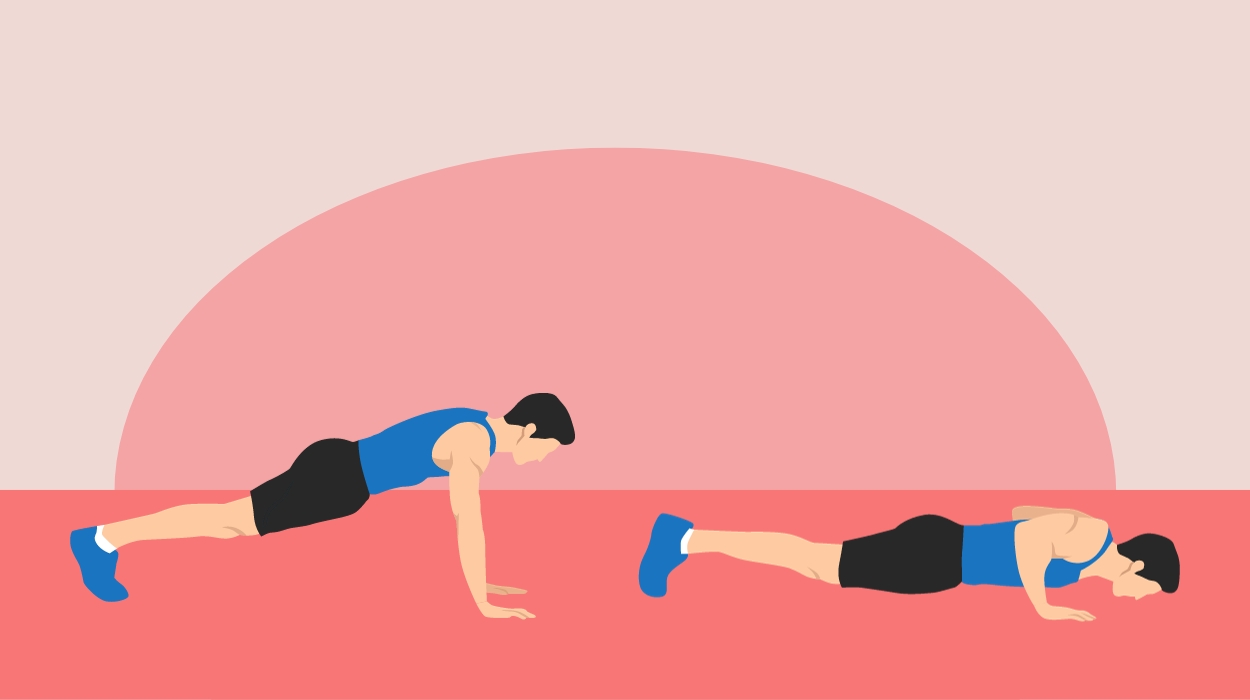

How To Do:
- Start on all fours with your hands spread slightly wider than your shoulders.
- Extend your legs backward until your feet are hip-width apart and your weight is resting equally on your hands and toes. Keep a slight bend in your elbows to avoid locking your arms as you do this.
- Once in this high plank position, tighten your core by sucking your belly button toward your spine.
- Inhale as you bend your arms at the elbows and slowly lower your body toward the floor, keeping your torso strong and rigid.
- When your elbows are at a 90-degree angle, exhale and use your arm strength to push your body back up into the high plank position.
Tips:
- Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels, engaging your core and glutes.
- Exhale as you push yourself up and inhale as you lower your body to maintain control and energy.
- Try variations like diamond push-ups or decline push-ups to continually challenge your muscles.
Optimal Sets & Reps: 3 sets of 8-12 reps.
What Causes Excess Arm Fat?
Chubby arms are a common concern with a variety of potential causes. Weight gain, weight loss, age, and genetics can all contribute to upper arm fat. For many people, excess arm fat is a result of being overweight, as around 85% of body fat is stored beneath the skin.[6]
In other cases, flabby arms are caused by weight loss. Significant weight loss can create loose skin[7] around body parts that were previously filled with fat tissue. People who lose weight may reduce arm fat only to be left with sagging skin that creates the appearance of ‘bat wings’ in their underarm area.
Your body fat distribution is also heavily influenced by your genetic makeup.[8] This means some people are more likely to store fat under their arms than others are, which is why they may find it harder to lose weight in this area. However, you can still reduce underarm fat with exercise and a calorie deficit diet, even if you are genetically predisposed to store fat here.
Finally, aging can contribute heavily to the appearance of flabby arms. As we age, our skin loses elasticity[9] and starts to droop. This can cause certain body parts such as the arms, chin, and belly to sag more, regardless of a person’s body weight.
Tips To Prevent Unwanted Arm Fat

Extra arm fat is usually caused by a surplus of subcutaneous fat. Subcutaneous fat sits just beneath the skin and, unlike visceral fat (which wraps around the internal organs) is considered relatively harmless.[10] However, if you are overweight, it can contribute to unwanted bumps and bulges in various body parts.
Therefore, the easiest way to prevent unwanted arm fat is with regular exercise and a healthy diet. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats combined with a physically active lifestyle can help you maintain a healthy body weight and a slim figure. If you are one of the many people who struggle with weight loss, you may also want to consider a dietary supplement to help lose stubborn body fat.
Fat-burning supplements containing active ingredients like caffeine and green tea extract have been scientifically proven to boost metabolism.[11] Increasing your metabolism raises the amount of energy your body uses at rest, which may aid in weight loss. When combined with regular exercise and a balanced diet, dietary supplements can help to reduce stubborn body fat.
The Bottom Line
Large arms are very common, which is why plenty of people want to know how to reduce arm fat and underarm flab. Fortunately, there are lots of ways to lose arm fat and tone loose skin in your upper limbs. If you are overweight or obese, losing arm fat can be as simple as reducing your overall body weight with regular cardio and a calorie-deficit diet.
For people with naturally large arms or loose skin, strength training exercises can target arm fat by toning your biceps and triceps. Workouts such as bicep curls, push-ups, and triceps dips can help make your upper arms look lean and muscular and reduce the appearance of arm fat.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some people are genetically predisposed to store more fat in their limbs than others. If you are one of these people, losing arm fat may be a challenge, although it is still possible with regular exercise and a healthy diet.
Lots of people want to lose arm fat fast, but the time it takes to slim down depends on your starting weight. If you’re just a little overweight, you may see improvement after a few weeks of regular exercise.
The key to reducing arm fat is reducing your overall body fat percentage. You can do this without gaining muscles by focusing on cardiovascular exercises like running, swimming, cycling, hiking, or dancing.
Working out with dumbbells will increase muscle mass in your upper arms and can help to tone loose skin and reduce the appearance of arm fat. Cardiovascular exercise is more effective for burning calories and fat loss than strength-training workouts.
Women naturally have a higher overall body fat percentage than men,[12] but we all lose weight in the same way, with a healthy, balanced diet, cardiovascular exercise, and strength training workouts.
 Evidence Based
Evidence Based
